

the diagram borrowed from the linked question probably explains it more succinctly:Īll that information stored in the inode can be accessed via stat() system calls, as per Linux man 7 inode:Įach file has an inode containing metadata about the file. an inode is unique on its own fileystem, but with multiple filesystems attached, you have non-unique inodes ). (Note, though that /dev and /run are virtual filesystems, so since they are root folders for their filesystem, they also have inode 2 i.e. Most famous is the inode #2 which is / directory. So each directory contains its own inode number, and then filenames and their inode numbers. a directory itself is a data structure, more specifically: a list of objects (files and inode numbers) pointing to lists about those objects (permissions, type, owner, size, etc.). So it has been there since the beginning.ĭirectory and inode pairing is also explained in How are directory structures stored in UNIX filesystem?. The first word is the i-node of the file represented by the entry, if non-zero if zero, the entry is empty. The fact that a file is a directory is indicated by a bit in the flag word of its i-node entry.ĭirectory entries are 10 bytes long.

#Q DIR LINUX MANUAL#
The 1971 manual on format of directories states: but there's no mention of inodes anywhere in the talk. (A directory is sometimes called a catalog in other systems.)" ".directory is actually no more than a file, but its contents are controlled by the system, and the contents are names of other files. And then some of those files, were directories which just contained name and I-number.Īn interesting observation can be made from Dennis Ritchie's talk in 1972 that Unix's notion of a directory is as Ken Thompson put it in a 1989 interview: Open programs also have inode tables, but that's not our concern for now. That object is called inode or I-number, and stored on disk in the inode table. In reality, a name (be it a directory or file, or whatever else) is just a string of text - a property of the actual object. Well, what users often understand as file is this: /etc/passwd - An object with a path and a name. You may have heard the expression "Everything is a file" for Unix/Linux.
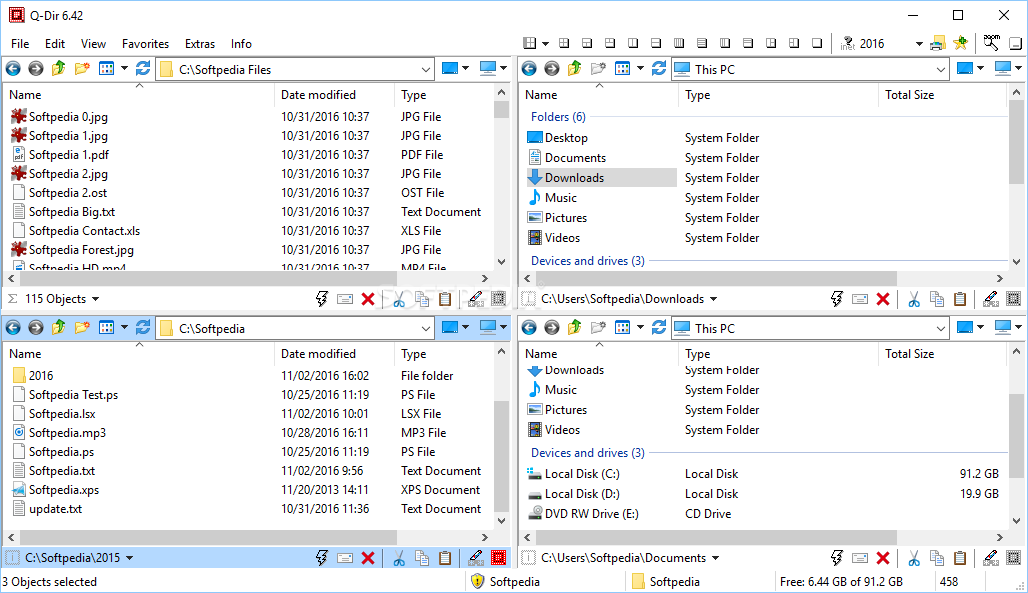
Understanding Unix/Linux filesystem and files: Everything is an inodeĮssentially, a directory is just a special file, which contains list of entries and their ID.īefore we begin the discussion, it's important to make a distinction between a few terms and understand what directories and files really represent. Once you have finished installing Q-Dir and started it for the first time, it will open with all four viewing panes active.Note: originally this was written to support my answer for Why is the current directory in the ls command identified as linked to itself? but I felt that this is a topic that deserves to stand on its own, and hence this Q&A.
#Q DIR LINUX INSTALL#
The second window asks if you would like to install for all users or just for the current account, the Program Group that you would like Q-Dir in, after-installation preferences, shortcut preferences, desired Target Directory, and an option to create a portable install ( nice!). The first window lets you choose the language version that you prefer by clicking on the appropriate flag symbol and has the EULA for Q-Dir.
#Q DIR LINUX WINDOWS#
The install process is extremely quick and easy with Q-Dir…there are only two windows to go through. Note: Q-Dir is available in regular install and portable versions. Now you can manage your files with up to four viewing panes at once with Q-Dir. Sometimes when looking through a file manager, it would be nice to have more than a dual-pane view.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
